PLASMA
GASIFICATION!
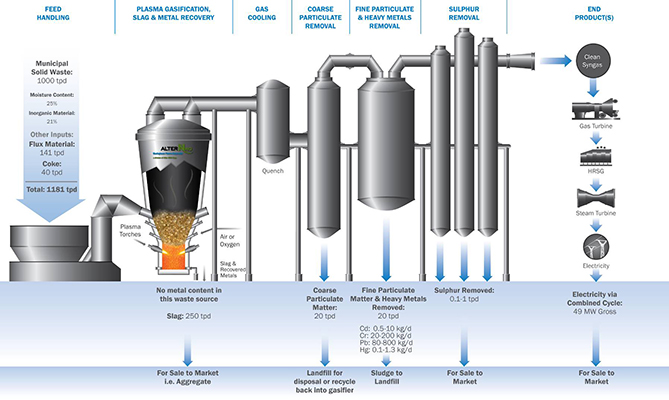
WPP's plasma gasification process converts the
organic waste into a fuel gas that still contains all the chemical and heat
energy from the waste. It converts the inorganic waste into an inert vitrified
glass, ethanol, biogas, biodiesel, and other various clean fuels with less
emissions and much higher efficiency.
Plasma is considered a 4th state. Electricity is fed to a torch, which has two
electrodes, creating an arc. Inert gas is passed through the arc, heating the
process gas to internal temperatures as high as 25,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The
following diagram illustrates how the plasma torch operates.
The temperature a few
feet from the torch can be as high as 5,000-8000º F. Because of these high
temperatures the waste is completely destroyed and broken down into its basic
elemental components. There are no tars or furans. At these high temperatures
all metals become molten and flow out the bottom of the reactor. In-organics
such as silica, soil, concrete, glass, gravel, etc. are vitrified into glass and
flow out the bottom of the reactor. There is no ash remaining to go back to a
landfill.
The plasma reactor does not discriminate between types of waste. It can process
any type of waste. The only variable is the amount of energy that it takes to
destroy the waste. Consequently, no sorting of waste is necessary and any type
of waste, other than nuclear waste, can be processed.
The reactors are large and operate at a slightly negative pressure, meaning that
the feed system is simplified because the gas does not want to escape. The gas
has to be pulled from the reactor by the suction of the compressor. Each reactor
can process 20 tons per hour (tph) compared to 3 tph for typical gasifiers.
Because of the size and the negative pressure, the feed system can handle
bundles of material up to 1 meter in size. This means that whole drums or bags
of waste can be fed directly into the reactor making the system ideal for large
scale production.
The gas composition coming out of a plasma gasifier is lower in trace
contaminants than with any kind of incinerator or other gasifier. Because the
process starts with lower emissions out of the reactor it is able to achieve
significantly lower stack emissions. The gasifier doesn't care about the amount
of moisture in the waste. The moisture consumes energy to vaporize and can
impact the capacity and economics, however, it will not affect the process.
Waste Gasification
|
Biomass Gasification
|
Plasma Gasification
|
Bio-fuel & Power
|
Potable Water |
Pyrolysis |
Financing |
About us |
Contact us
|

